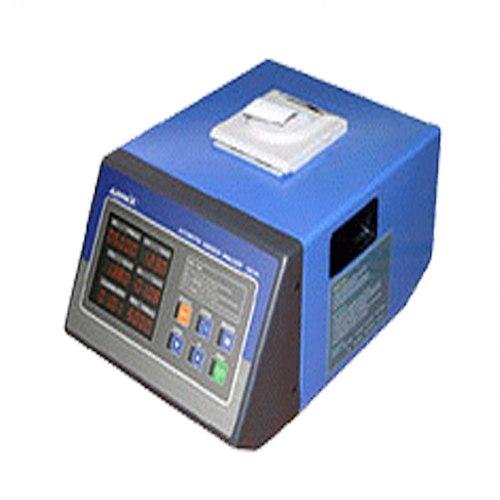
Exhaust Gas Analyzer (VPL-AML-EGA)
Exhaust Gas Analyzer (VPL-AML-EGA)
Features
- ARAI Approved
- High Quality SMPS operated from 90volts to 270volts
- Very low electric consumption
- Heat resistant silicon tubes
- High quality water separator
- 32bit Micro – Processor
- Electromagnetic field resistant
- On board Atmospheric pressure sensor
- Voltage drops, spike
- High quality display
Technical Specifications
- Measure Range (Resolution)
- Warm up time : less than equal to 3min
- Auto Zero : 20sec
- Fuel selectable (Petrol / LPG / CNG)
- Leakage Test
- HC Residual Test
- Measured items – HC, CO, CO2, O2 Lambda/AFR
- Basic Accessories : Probe, Fuse, Leak Test Cap, Dust Filter, Carbon Filter, Power Cord
DIFFERENT SENSORS OF CAR
MAP (Manifold Air Pressure) Sensor
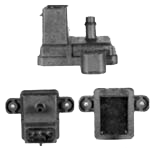 The MAP sensor is a pressure sensor chip which puts out a voltage proportional to engine vacuum, from zero to 5 volts. The computer uses the voltage to decide if the throttle is open and how far, so it can adjust the fuel mixture.
The MAP sensor is a pressure sensor chip which puts out a voltage proportional to engine vacuum, from zero to 5 volts. The computer uses the voltage to decide if the throttle is open and how far, so it can adjust the fuel mixture.
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
 The Throttle Position Sensor is a potentiometer (variable resistor) which attaches to the throttle shaft and sends a voltage signal to the computer, telling it how far open the throttle is. The resistance across it is about 5,000 ohms. At idle the voltage is about 0.7 V and wide open throttle is about 4.0 V. You can measure the voltage with ignition on and engine off, using a voltmeter.
The Throttle Position Sensor is a potentiometer (variable resistor) which attaches to the throttle shaft and sends a voltage signal to the computer, telling it how far open the throttle is. The resistance across it is about 5,000 ohms. At idle the voltage is about 0.7 V and wide open throttle is about 4.0 V. You can measure the voltage with ignition on and engine off, using a voltmeter.
Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS)
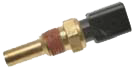 The Coolant Temperature Sensor is a thermistor (temperature-dependent variable resistor) which screws into the thermostat housing and sends a voltage signal to the computer, telling it the coolant temperature. The resistance across it is about 13,000 ohms with engine off at room temperature.
The Coolant Temperature Sensor is a thermistor (temperature-dependent variable resistor) which screws into the thermostat housing and sends a voltage signal to the computer, telling it the coolant temperature. The resistance across it is about 13,000 ohms with engine off at room temperature.
Heated Oxygen Sensor
 The Oxygen Sensor is a feedback device that senses how much oxygen is in the exhaust. The zirconium coating in the sensor produces a small voltage when exposed to depleted levels of oxygen, so a lean exhaust which has
The Oxygen Sensor is a feedback device that senses how much oxygen is in the exhaust. The zirconium coating in the sensor produces a small voltage when exposed to depleted levels of oxygen, so a lean exhaust which has
excess oxygen yields a signal of about 0.2 V, whereas a rich mixture (all oxygen consumed) produces over 0.7 V.
Air Temperature Sensor (IAT)
![]() The intake air temperature sensor (IAT) tells the ECM the temperature of the air that is going into the engine. The cooler the air, the better the performance of the engine, which is probably why you might have noticed a difference in the car’s performance on a summer night as compared to the day.
The intake air temperature sensor (IAT) tells the ECM the temperature of the air that is going into the engine. The cooler the air, the better the performance of the engine, which is probably why you might have noticed a difference in the car’s performance on a summer night as compared to the day.
Crankshaft Sensor (CKP)
 This sensor is very similar to the cam position sensor in functionality. It is responsible for telling the ECM the exact location of the crankshaft as well as the RPM (rotations per minute) of the engine. With this information the ECM knows the position of each piston in each cylinder.
This sensor is very similar to the cam position sensor in functionality. It is responsible for telling the ECM the exact location of the crankshaft as well as the RPM (rotations per minute) of the engine. With this information the ECM knows the position of each piston in each cylinder.
Idle Air Controller (IACV)
 The Idle Air Control Valve (IACV) is responsible for keeping the RPM of the engine steady. The IACV is actually an
The Idle Air Control Valve (IACV) is responsible for keeping the RPM of the engine steady. The IACV is actually an
actuator and not a sensor because it does not supply readings to the ECM, but works on the command of the ECM. I just added this actuator for the DIY enthusiast.
Note: Images given are for representation only and the final equipment can change according to its specifications.

